

The Comprehensive Guide to Machine Learning: Concepts, Algorithms, and Applications
Machine Learning
Ali Hamza
Machine learning is no longer a futuristic concept reserved for science fiction movies. It’s the unseen force behind the recommendations on your favorite streaming platforms, the voice assistant you talk to on your phone, and the alerts your bank sends when something looks suspicious. As the world produces more data than ever before, the power to understand it, learn from it, and act on it has become one of the most transformative drivers of change across every industry.
At its core, machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on building systems that learn from data. Instead of following strictly programmed rules, these systems improve their performance over time as they are exposed to more information. This capability is reshaping how businesses operate, how doctors diagnose diseases, and how we interact with technology daily.
This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for understanding this complex field. Whether you are a business leader looking to implement automation or a student starting your journey, we will break down the essential machine learning concepts. We will explore how it works, the different types of learning models, key algorithms, and the tools used to build them. By the end of this machine learning guide, you will have a solid grasp of the technology defining the modern digital era.
What is Machine Learning?
To understand machine learning in simple terms, think about how a child learns to recognize a dog. You don’t teach a child by giving them strict rules like, “If it has four legs and barks, it’s a dog.” Instead, you show them many pictures of dogs. Over time, the child begins to notice patterns such as floppy ears, fur, or a snout and can eventually identify a dog they’ve never seen before.
Machine learning works in much the same way. It allows computers to learn from data rather than following fixed instructions. Instead of being explicitly programmed step by step, machines analyze examples, detect patterns, and make decisions on their own.
In traditional programming, a developer writes detailed rules that tell a computer exactly how to process input data to produce a specific output. With machine learning, the system learns those rules for itself by studying data.
Traditional Programming vs. Machine Learning:
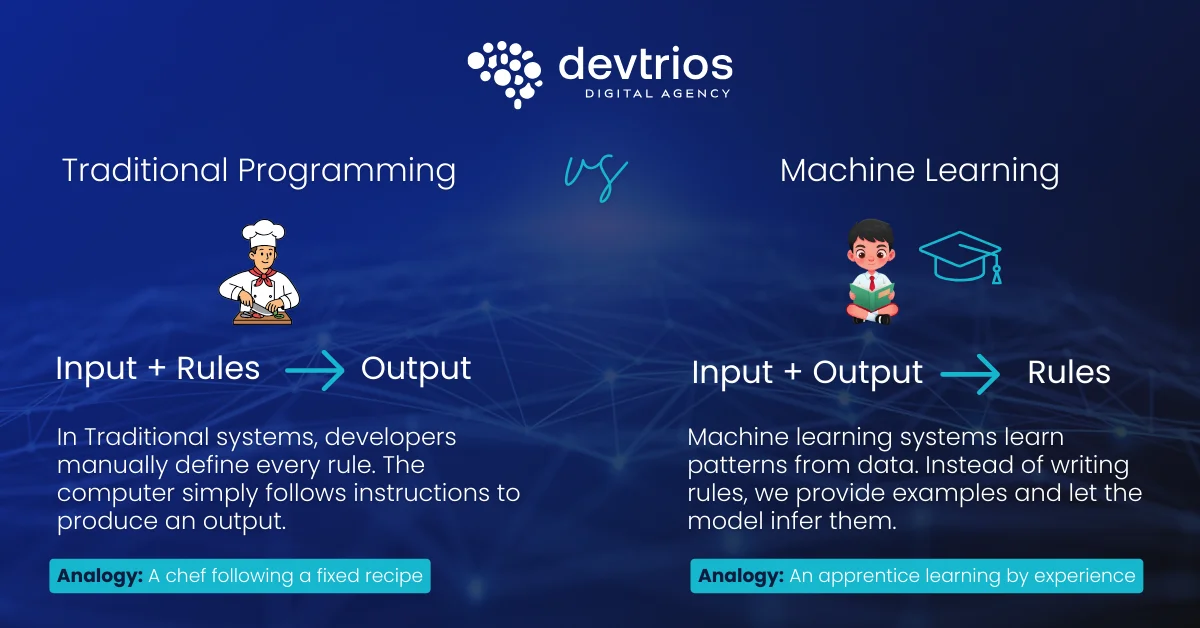
- Traditional Programming: Data + Rules = Answers
- Machine Learning: Data + Answers = Rules
In a machine learning model, you feed the computer input data and the corresponding output data. The algorithm then analyzes this relationship to create a “rule” or a model. This model can then take new, unseen data and predict the correct output.
Learn & Master AI / Machine Learning
Explore neural networks, classification, clustering, and real-world AI applications. Our experts guide you with practical examples, insights, and strategies to help you build, analyze, and implement AI solutions effectively.
Get Expert AI Guidance →Analogy: The Chef vs. The Apprentice
Traditional programming is like a master chef following a precise recipe. Every step is clearly defined if the recipe says to add five grams of salt, that’s exactly what the chef does. The result is consistent and predictable, but it leaves little room for flexibility.
Machine learning, on the other hand, is more like an apprentice chef learning through experience. They taste the soup, notice it’s missing something, add a pinch of salt, taste again, and keep adjusting until it’s just right. Instead of following fixed instructions, the apprentice learns from feedback the “data” and improves their approach over time to achieve the best possible outcome.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is machine learning? | It is a field of AI where computers learn from data to identify patterns and make decisions with minimal human intervention. |
| How does machine learning work? | It uses algorithms to parse data, learn from it, and then make a determination or prediction about something in the world. |
Why Machine Learning Matters
The significance of machine learning cannot be overstated. It is the bridge between raw data and actionable intelligence. As organizations gather enormous amounts of data from customer clicks on websites to sensor readings in factory equipment, machine learning offers the only practical way to make sense of it at scale.
One of the biggest benefits of machine learning is efficiency through automation. Algorithms can quickly process documents, sort emails, and respond to customer service inquiries with speed and accuracy that often surpass human capabilities. This allows people to shift their focus to more creative, strategic work that relies on critical thinking and emotional intelligence.
Key Benefits
- Personalization: Companies like Netflix and Amazon use ML to analyze your behavior and suggest products or movies you will likely enjoy.
- Insight Discovery: ML algorithms can find hidden patterns in data that humans might miss, such as a subtle correlation between weather patterns and retail sales.
- Operational Efficiency: Predictive maintenance in manufacturing uses ML to predict when a machine will break down before it happens, saving millions in downtime.
Real-World Impact
In healthcare, machine learning is helping save lives by analyzing medical images and identifying tumors earlier often with greater accuracy than the human eye alone. In finance, algorithms analyze transaction patterns in milliseconds to flag fraudulent activity, protecting consumer assets. In marketing, brands use predictive analytics to anticipate customer needs, delivering the right message at the exact right moment.
Types of Machine Learning
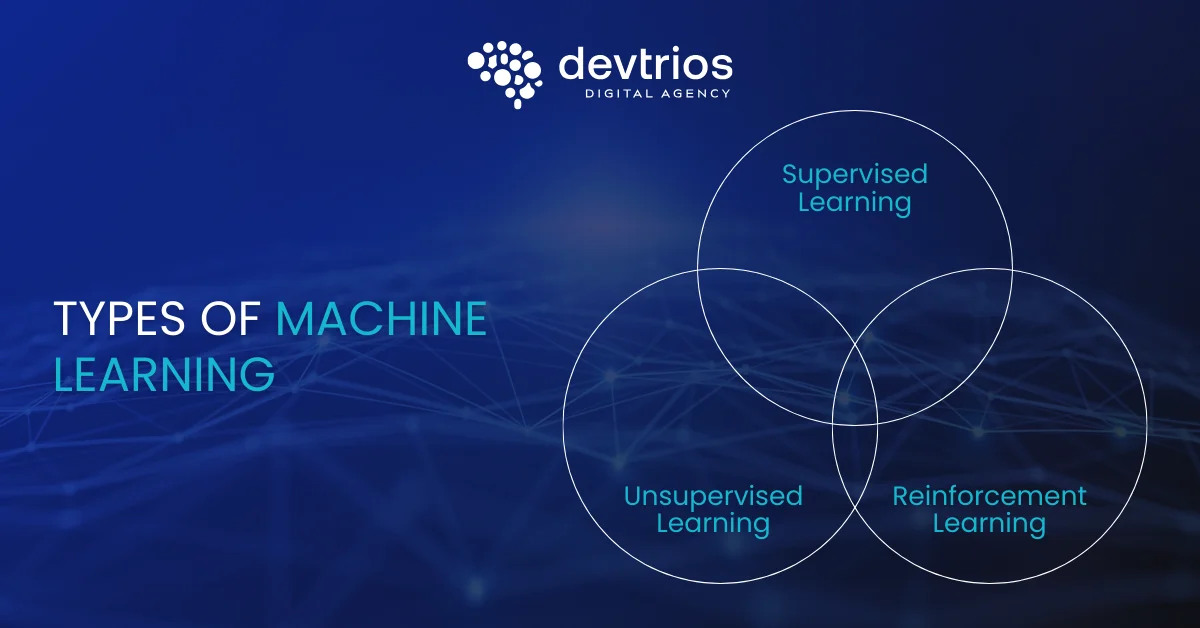
1. Supervised Learning
This is the most common type of machine learning. In supervised learning, the algorithm is trained using labeled data that already comes with the correct answers.
For example, when training a model to detect spam emails, you provide thousands of emails that are clearly marked as “spam” or “not spam.” The model learns how different patterns in the email content relate to each label.
Once the training is complete, you can give the model a brand-new email it has never seen before, and it will predict whether that message is spam or not.
Examples:
- Image recognition
- Price prediction (Regression)
- Spam filtering
2. Unsupervised Learning
In this case, the data comes without labels. The system is given a large amount of information and must discover patterns and relationships on its own there’s no predefined “right” answer. The goal is to explore the data and uncover natural groupings within it.
A simple way to think about this is to imagine giving a child a bucket full of mixed Lego bricks and asking them to organize them. The child might sort the pieces by color, size, or shape. In the same way, the algorithm decides how to structure the data based on what it finds.
Examples:
- Customer segmentation (grouping customers by purchasing behavior)
- Anomaly detection (finding weird data points in security logs)
- Recommendation engines
3. Reinforcement Learning
This type of learning is driven by behavior. The algorithm, often called an agent learns by interacting with its environment and receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties. Through trial and error, it gradually figures out which actions lead to the best overall outcome.
You can think of it like training a dog. When the dog sits on command, it gets a treat as a reward. If it doesn’t, there’s no reward. Over time, the dog learns that sitting leads to a positive result and adjusts its behavior accordingly.
Examples:
- Robotics (learning to walk or grasp objects)
- Game playing (AlphaGo, chess engines)
- Self-driving cars
Machine Learning Algorithms
Algorithms are the mathematical engines that drive machine learning. There are dozens of machine learning algorithms, but most fall into a few key categories depending on the task at hand.
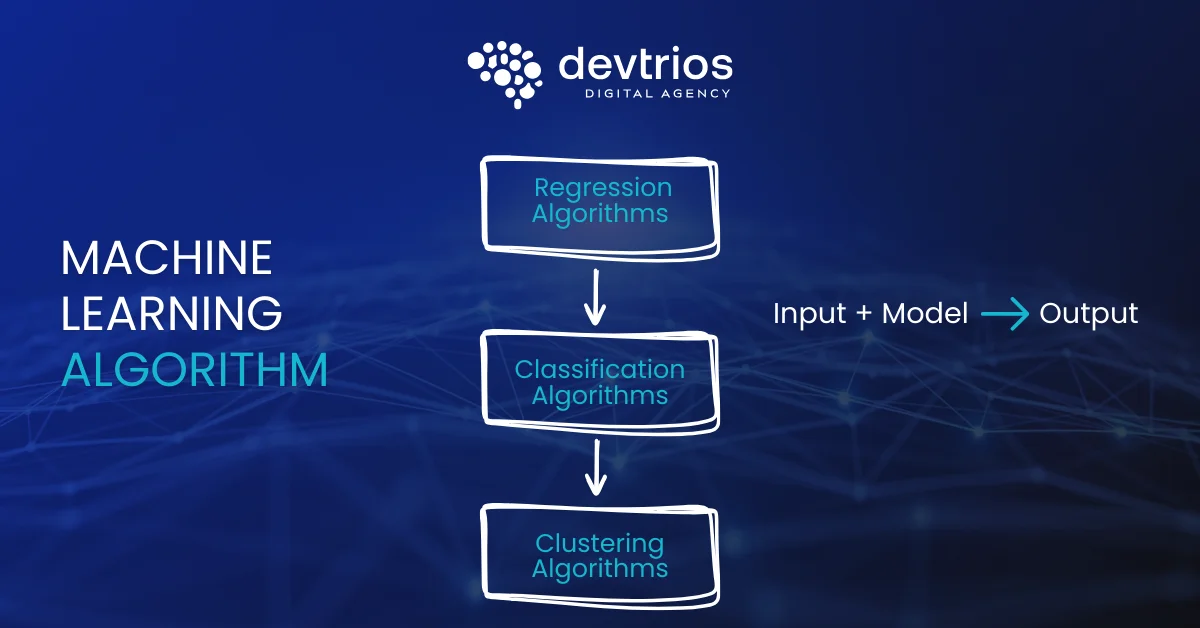
Regression Algorithms
Regression is used when the output variable is a continuous value, like a number.
- Linear Regression: One of the simplest common machine learning algorithms. It finds a line that best fits the data points to predict a value.
- Real-life example: Predicting house prices based on square footage and location.
Classification Algorithms
Clustering Algorithms
Neural Networks and Deep Learning

Inspired by the way the human brain works, neural networks are made up of layers of interconnected nodes, often called neurons, that work together to process information.
In everyday life, neural networks power technologies like language translation tools and facial recognition systems used in security and authentication.
Machine Learning Tools & Technologies
You do not need to build these algorithms from scratch. A robust ecosystem of machine learning tools and libraries exists to help developers and data scientists build models efficiently.
Primary Languages
Python is the undisputed king of machine learning software development due to its simplicity and vast library support. R is also popular, particularly in academia and statistical analysis.
Key Frameworks and Libraries
- Scikit-learn:
- Best for: Beginners and classic ML algorithms (regression, clustering).
- Features: Easy to use, excellent documentation, handles data preprocessing well.
- TensorFlow:
- Best for: Deep learning and neural networks.
- Features: Developed by Google, it is powerful, scalable, and used for production-grade AI applications.
- PyTorch:
- Best for: Research and deep learning.
- Features: Developed by Facebook (Meta), it is known for its flexibility and dynamic computation graph, making it a favorite among researchers.
- Pandas & NumPy:
- While not ML libraries per se, these are essential for data manipulation and mathematical operations before feeding data into machine learning frameworks.
Applications of Machine Learning
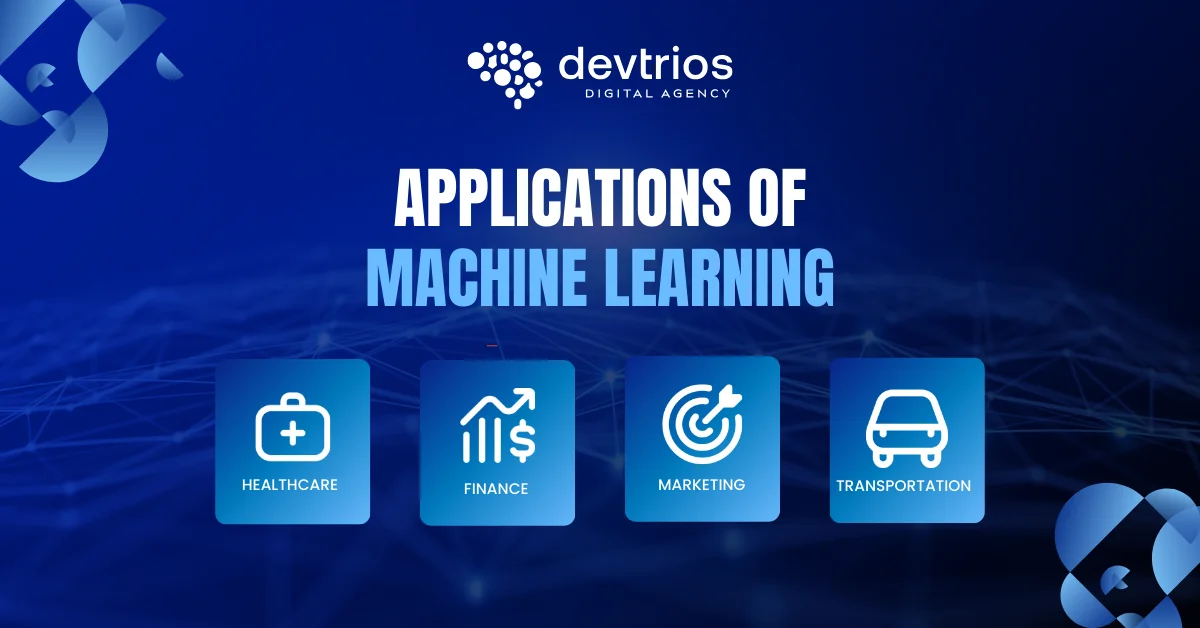
The versatility of machine learning use cases means it touches nearly every sector of the global economy. Here is how different industries are leveraging these machine learning applications:
Healthcare
ML is revolutionizing patient care. Algorithms analyze historical patient data to predict outbreaks of chronic diseases. In radiology, AI models assist doctors by highlighting potential anomalies in X-rays and MRIs with incredible precision. Drug discovery is also being accelerated, with ML predicting how different molecules will interact, cutting years off the development process.
Finance
Financial institutions were early adopters. High-frequency trading algorithms execute thousands of trades per second based on market data. Banks use credit scoring models that analyze thousands of data points beyond just payment historyto assess borrower risk more accurately.
Marketing and Sales
Personalization is the key here. From “Recommended for You” emails to dynamic pricing on airline websites, ML drives conversion. Chatbots powered by Natural Language Processing (NLP) handle customer service 24/7, resolving routine issues instantly.
Transportation and Autonomous Systems
Self-driving cars are perhaps the most famous application. They use computer vision (a type of ML) to recognize lane markers, pedestrians, and traffic signs. Logistics companies use ML to optimize delivery routes in real-time based on traffic and weather, saving fuel and time.
Career Paths in Machine Learning
As demand for AI grows, so does the demand for skilled professionals. A machine learning career is currently one of the most lucrative and secure paths in tech.
Salary Range: $120,000 - $180,000+
Salary Range: $100,000 - $160,000+
Essential Skills
To succeed, you need a mix of technical and soft skills:
- Programming: Python, R, SQL.
- Math: Linear algebra, calculus, probability, and statistics.
- Data Engineering: Understanding how to clean and pipeline data.
- Soft Skills: Problem-solving and the ability to explain complex technical findings to non-technical stakeholders.
Learning Machine Learning
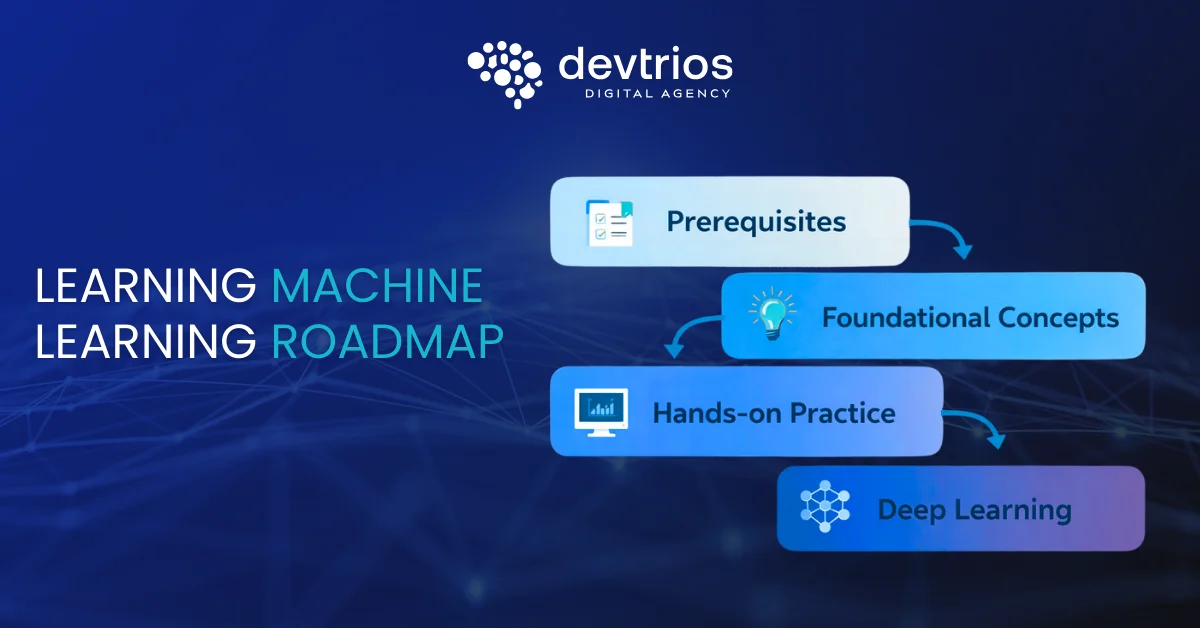
The Roadmap
- Prerequisites: Ensure you have a grasp of Python programming and high-school level statistics/algebra.
- Foundational Concepts: Start with a machine learning tutorial on basic algorithms like linear regression and decision trees.
- Hands-on Practice: Use platforms like Kaggle to participate in competitions. Kaggle provides datasets and a community to learn from.
- Deep Learning: Once comfortable with the basics, move on to neural networks using TensorFlow or PyTorch.
Recommended Resources
- Online Courses: Coursera (Andrew Ng’s Machine Learning course is legendary), edX, and Udacity offer specialized nanodegrees.
- Certifications: Google’s Professional Machine Learning Engineer or AWS Certified Machine Learning – Specialty can validate your skills to employers.
- Books: “Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow” is widely considered the bible for practitioners.
Conclusion
Machine learning is not just a buzzword; it is a fundamental shift in how we process information and solve problems. From automating mundane tasks to diagnosing complex diseases, the ability to learn machine learning principles is becoming a critical skill in the modern workforce.
Mastering these concepts requires patience and practice, but the rewards are immense. Whether you are looking to pivot your career or simply understand the technology shaping your world, the journey into machine learning opens up endless possibilities for innovation. As algorithms become more sophisticated, staying informed and educated on these foundations will be key to navigating the future of technology.
Want to Master AI & Machine Learning?
Explore practical insights, hands-on examples, and expert guidance on neural networks, clustering, classification, and more. Learn how to build, analyze, and implement AI solutions effectively.
Get Expert AI Guidance →FAQ / People Also Ask
What is machine learning?
How does machine learning work?
What are the main types of machine learning?
What are the top machine learning algorithms?
How is machine learning used in real life?
About This Guide
This guide is written by Ali Hamza, based on industry research and real-world insights into AI and Machine Learning. It covers key concepts, practical examples, algorithms like classification, clustering, neural networks, and roles in AI to help learners understand and implement AI effectively.
The goal of this guide is to provide clear, actionable, and easy-to-understand information for students, professionals, and AI enthusiasts to learn ML concepts, explore real-life applications, and make informed decisions when building AI solutions.
View Author Profile


