

People Also Search For: The Complete SEO Guide to Google’s Most Underutilized SERP Feature
SEO
Ali Hamza
When you search for a topic on Google, click a link, and immediately hit the back button, you’ve triggered one of Google’s most valuable yet overlooked SERP features: People Also Search For (PASF). This feature displays 6–8 related search queries that other users have searched for after exploring your clicked result. Unlike flashy featured snippets or prominent People Also Ask boxes, PASF operates quietly in the background, yet it’s a goldmine of keyword research data, content gap analysis, and SEO opportunity that most marketers ignore.
Key Insight: PASF represents the #1 untapped keyword opportunity in SEO. While 95% of competitors focus on paid keywords and featured snippets, PASF data is free, behavior-based, and reveals exactly what users want when they don’t find your content satisfying.
People Also Search For isn’t just a convenience feature for searchers it’s a direct window into user intent, search behavior patterns, and the topics your audience cares about most. For SEO professionals, content strategists, and digital marketers, PASF represents untapped keyword clusters, long-tail opportunities, and quick wins for content optimization. This guide will walk you through what PASF is, how it works, why it matters for SEO, and how to leverage it alongside AI and NLP tools to build comprehensive, authority-signaling content strategies.
What Is People Also Search For (PASF)
People Also Search For is a Google SERP feature that appears after a user clicks on a search result and returns to the Google search results page. When Google detects this behavior what SEO professionals call “pogo-sticking” it displays a box containing 6 to 8 alternative search terms below the result the user just abandoned.
How Google's People Also Search For Feature Works
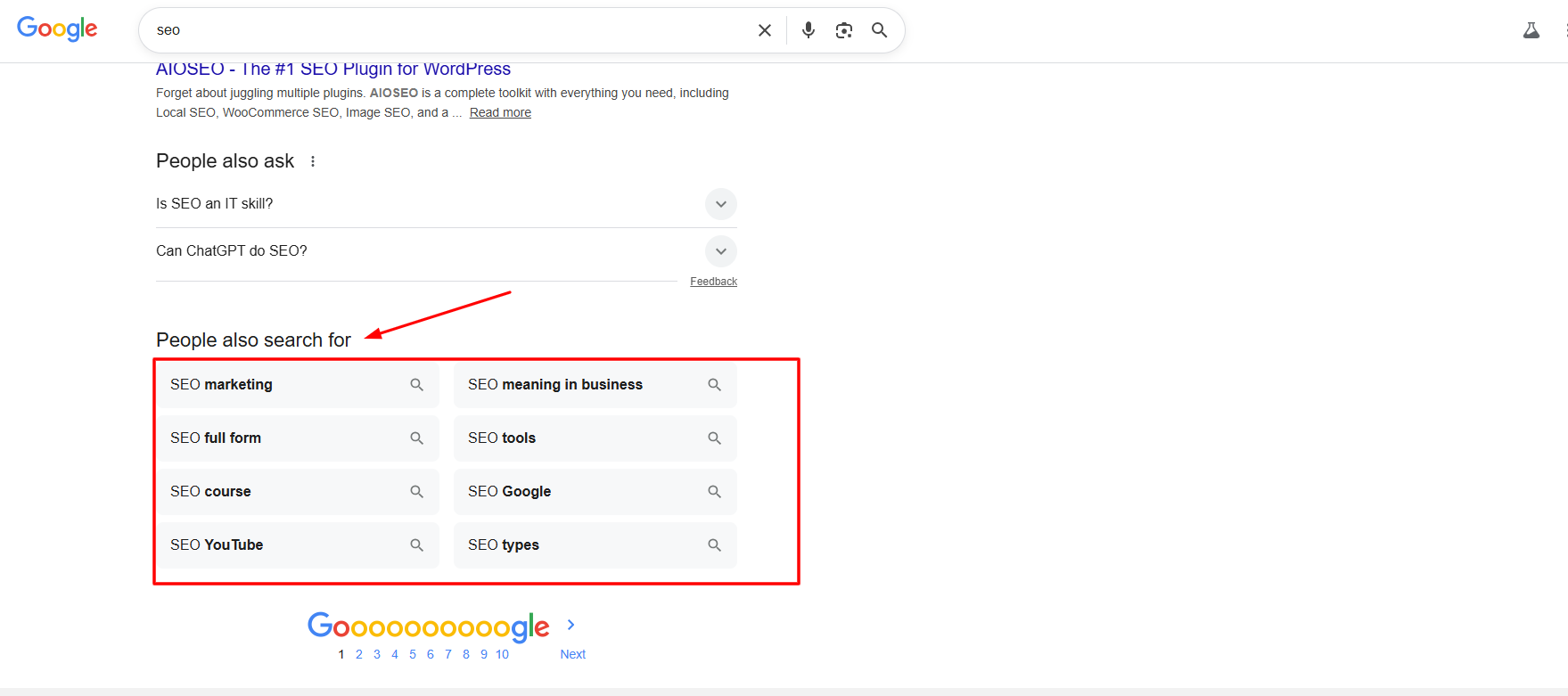
PASF operates on a deceptively simple principle: if a user bounced back to Google from a result, they likely didn’t find what they needed. Google’s algorithm interprets this pogo-stick behavior as a signal that the user wants to refine, pivot, or broaden their search. The system then surfaces related queries that other users have searched for after visiting that same URL.
The triggering mechanism:
- User searches “organic face cream”
- User clicks result from skincare site
- User returns to Google within 10-30 seconds (bounce signal)
- Google displays 6-8 PASF keywords related to “organic face cream”
- Other users see these alternatives and may click one instead
The PASF data itself comes directly from Google’s massive search database, meaning the keywords shown are based on real, aggregated search patterns—not predictive algorithms or manufactured suggestions. This makes PASF data extraordinarily valuable for understanding:
- Search behavior at scale: What do users actually search for next?
- Content relevance gaps: What information are users looking for that they didn’t find?
- Topical relationships: How are keywords semantically and behaviorally connected?
- Intent shifts: How does user intent evolve within a topic cluster?
PASF vs. PAA vs. Related Searches vs. Autocomplete: Understanding the SERP Feature Landscape
Marketers often conflate these four Google features, but each serves a distinct purpose and occupies a different SERP position. Understanding these differences is crucial for a comprehensive SEO strategy.
| Feature | PASF | PAA | Related Searches | Autocomplete |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trigger | Bounce / Back Button | Direct SERP Display | SERP Scroll | Real-time Typing |
| Format | Related Keywords | Q&A Boxes | Keyword Suggestions | Predictive Queries |
| Position | Right Side or Bottom | Below Featured Snippet | Bottom of SERP | Dropdown in Search Bar |
| Update Frequency | Dynamic (User-triggered) | Evolves with Queries | Less Dynamic | Constantly Updated |
| Primary Use | Keyword Expansion | FAQ Targeting | Secondary Discovery | Quick Suggestions |
| Ranking Opportunity | Indirect (Content Alignment) | Featured Snippets | Organic Results | Organic Results |
Critical distinction: PASF is behavioral and reactive (user-triggered), while PAA is algorithmic and proactive (always displayed for relevant queries). PASF responds to what users don’t find, while PAA anticipates what users will ask.
Best Practice: Don’t choose between PASF and PAA optimization use both. PASF data reveals keyword expansion opportunities; PAA reveals question-based content gaps. Together, they create comprehensive content strategies.
The PASF vs. PAA comparison is particularly important: while PAA focuses on answering questions with featured snippets, PASF reveals the next search a user wants to make after their question wasn’t fully answered.
Why People Also Search For Keywords Matter for SEO

PASF keywords represent one of SEO’s most underexploited opportunities. Here’s why they’re critical to modern search strategies:
1. Instant Long-Tail Keyword Discovery
Long-tail keywords those 3+ word phrases with lower search volume but higher intent specificity are where conversion and topical authority live. PASF eliminates the guesswork by showing you exactly which long-tail variations users are searching for.
Real example from organic skincare niche:
- Primary keyword: “organic face cream”
- PASF keywords revealed:
- Fair trade organic face cream
- Best organic face cream for sensitive skin
- Organic face cream with SPF
- Affordable organic face cream
- Organic face cream for acne-prone skin
- Best organic face cream for anti-aging
Analysis: Each PASF keyword targets a different user intent and market segment. “Fair trade” appeals to ethical consumers; “sensitive skin” targets dermatological concern; “affordable” captures price-conscious buyers. Manual keyword research would take 20+ hours; PASF reveals them in 2 minutes.
2. Content Gap Analysis and Topic Clustering
Every PASF keyword represents a content gap or an unaddressed user need. If users are bouncing from your page and searching for “best organic face creams for acne” when they landed on your general “organic skincare” post, you’ve identified a gap.
Content audit framework:
- Search your primary keyword on Google
- Click on your top-ranking result (or competitor’s)
- Return to Google and note PASF keywords
- Check if your content addresses each topic
- Create new sections, FAQ items, or linked pages for gaps
This process creates natural topic clusters and pillar-page structures that Google rewards with improved topical authority signals. [See Topic Cluster diagram in visuals section]
3. User Intent Alignment and Relevance Signals
Google’s core ranking systems prioritize content that matches user intent. PASF keywords reveal the specific questions, pain points, and variations users care about within your topic.
When you incorporate PASF keywords into your content, you’re essentially saying to Google: “I understand all the ways users approach this topic, and I address each variation.” This alignment improves:
- Dwell time (users find answers faster)
- Page engagement (more internal links, scrolls, time on page)
- Return visits (users perceive your site as comprehensive)
- Semantic relevance (your content maps to multiple query variations)
4. Multi-SERP Feature Ranking Opportunities
PASF keywords often overlap with PAA questions and featured snippet targets. By optimizing for PASF-derived keywords, you simultaneously improve your chances of capturing:
- Featured snippets (position zero, 42.9% CTR)
- PAA boxes (64.9% of searches now display PAA)
- AI Overviews sources (content cited in AI-generated answers)
- Knowledge panels (with proper entity markup)
This “stacking” of SERP features is one of the most effective ranking levers in 2025–2026.
How to Find People Also Search For Keywords: Complete Toolkit
Method 1: Manual Collection (Free, Time-Intensive)
Ideal for: Small-scale research, validation, understanding user behavior
Step-by-step process:
- Go to Google.com and search your target keyword
- Click on a result you want to analyze
- Immediately return to Google (hit back button)
- Note the PASF box that appears below the result
- Record all 6–8 keywords shown
- Repeat for multiple results (top 3-5 links)
Time investment: 5-10 minutes per keyword
Limitations: No volume or difficulty data; not scalable beyond 50 keywords
Method 2: Keywords Everywhere Browser Extension (Recommended for Solo Marketers)
Ideal for: Individual SEOs, content creators, continuous monitoring
Setup (3 steps):
- Install Keywords Everywhere for Chrome or Firefox
- Create account and receive API key via email
- Enter API key in extension settings
Features you get:
- PASF keywords displayed automatically on every Google search
- Search volume + CPC for each keyword
- Competition score (Low/Medium/High)
- Automatic keyword data export
- Browser history analysis
Cost: $10–50/month (most affordable solution)
Advantage: Shows volume and competition alongside PASF keywords, enabling instant prioritization
Method 3: Semrush Keyword Magic Tool (Best for Teams)
Ideal for: Agencies, teams, enterprise-scale research
How to access:
- Open Semrush → SEO Tools → Keyword Magic Tool
- Enter seed keyword
- Filter by “Related Keywords”
- Cross-reference with Organic Research reports
Advanced features:
- 26+ billion keyword database
- Automatic intent classification
- SERP feature identification
- Competitive analysis at scale
- Automated topic clustering
Cost: Starts at $117/month
Step-by-Step Content Optimization Using PASF Keywords

Phase 1: Keyword Collection & Categorization (Week 1-2)
Spreadsheet structure for tracking:
| PASF Keyword | Volume | Difficulty | Intent | Topic Cluster | Coverage | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| organic face cream acne | 1,200 | 35 | Commercial | Acne Solutions | Partial | High |
| best organic moisturizer dry skin | 890 | 42 | Commercial | Moisturizers | No | High |
| organic skincare routine beginners | 2,100 | 22 | Informational | Routines | Yes | Medium |
| organic face cream wholesale bulk | 320 | 28 | Transactional | B2B | No | Low |
Collection strategy:
- Start with 5-10 seed keywords
- Search each on Google 3-5 times
- Note PASF keywords each time
- Aggregate in spreadsheet with volume/difficulty data
- Categorize by intent and topic cluster
Phase 2: Content Audit & Gap Identification
Create a gap audit spreadsheet:
- For each page on your site:
- Record target keyword
- List main H2/H3 topics covered
- Check if PASF keywords are addressed
- Mark coverage levels:
- Full coverage: Dedicated section with deep explanation
- Partial coverage: Keyword mentioned but not explored
- No coverage: Keyword entirely absent
- Prioritize by impact:
- High volume + No coverage = Immediate priority (create new page or add section)
- Medium volume + Partial coverage = Expand existing content
- Low volume = Bundle into FAQ section
Phase 3: Content Creation & Optimization
Update Existing Content with PASF Sections
For articles with partial PASF coverage, add new H2/H3 sections:
xml
<!– ORIGINAL ARTICLE STRUCTURE –>
<h2>Best Organic Skincare Products</h2>
<h3>Cleansers</h3>
<h3>Moisturizers</h3>
<h3>Serums</h3>
—
<!– ENHANCED VERSION (incorporating PASF keywords) –>
<h2>Best Organic Skincare Products</h2>
<h3>Cleansers</h3>
<h3>Moisturizers</h3>
<h3>Serums</h3>
<!– NEW SECTIONS ADDRESSING PASF KEYWORDS –>
<h3>Best Organic Face Creams for Sensitive Skin</h3>
<p>Sensitive skin requires formulations free of common irritants like fragrance, sulfates, and essential oils. Top options include: [recommendations with links]</p>
<h3>Non-Toxic Anti-Aging Serums</h3>
<p>Natural alternatives to retinol and synthetic anti-aging ingredients…</p>
<h3>Organic Sunscreen SPF 30+</h3>
<p>Reef-safe, mineral-based sun protection for daily use…</p>
Key principles:
- Lead with PASF keyword in H3 (improves keyword relevance)
- Answer specific intent (not generic information)
- Include 300–500 words per section
- Add visuals (product images, comparison tables)
- Link to related pages (internal linking strategy)
Create Dedicated Pages for High-Intent PASF Keywords
When to create a standalone page:
- PASF keyword has 1,000+ monthly searches
- Clear commercial or transactional intent
- Not adequately addressed by existing content
- High revenue potential
Introduction (200 words)
├─ Define the problem
├─ Explain why conventional creams fail
└─ Promise solutions
H2: Comparison Table
├─ Brand, price, key ingredients, rating
└─ Quick-reference chart
H2: Top 5-7 Products
├─ Product reviews (pros/cons)
├─ Full descriptions
└─ Price ranges
H2: FAQ Section
├─ PASF-derived questions
├─ 40-60 word answers
└─ FAQ schema ready
H2: Buying Guide
├─ How to choose (ingredient guide)
├─ Price ranges
└─ Where to buy
H2: Related Products
├─ Internal links to cluster pages
└─ “Explore more” navigation
Phase 4: Implement FAQ Schema for Featured Snippets
FAQ schema signals to Google that your page answers specific questions, increasing featured snippet eligibility:
json
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "FAQPage",
"mainEntity": [
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "Do organic face creams really work for acne?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Organic face creams can be effective for acne when formulated with ingredients like salicylic acid alternatives, tea tree oil, or sulfur. However, effectiveness varies by skin type. Consult a dermatologist for persistent acne."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "Can you use organic face cream with acne medication?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "Yes, but choose non-comedogenic formulas. Avoid heavy oils and inform your dermatologist about all skincare products to prevent interactions."
}
}
]
}
Best practices:
- Add 5-10 FAQ items per page
- Make FAQs visible on page (not hidden)
- Keep answers concise (40-60 words)
- Use PASF keywords in question text
- Validate with Google’s Rich Results Test
Phase 5: Build Pillar Pages and Topic Clusters
Topic clusters amplify topical authority by linking a pillar page to cluster content.
Example structure for “Organic Skincare”:
Pillar Page: The Complete Guide to Organic Skincare (3,000-4,000 words)
- Links to all cluster pages
- Comprehensive overview
- Establishes site authority
Cluster Pages (from PASF keywords):
- Best Organic Face Creams for Sensitive Skin
- Organic Acne-Fighting Serums: Natural Alternatives
- How to Start an Organic Skincare Routine
- Organic vs Conventional Skincare: Science Comparison
- Where to Buy Organic Skincare Products [2025]
- Non-Toxic Anti-Aging Serums: Retinol Alternatives
Internal linking pattern:
- Pillar → Clusters (via “related posts,” resource lists)
- Clusters → Pillar (via “start here” navigation)
- Cluster ↔ Cluster (cross-topic navigation for related products)
Result: Improved crawlability, distributed authority, reduced cannibalization, and stronger topical authority signals.
Ready to Turn PASF Data Into Rankings & Traffic?
Stop guessing keywords and start leveraging Google's real user behavior data. Our SEO specialists help you uncover hidden People Also Search For opportunities, build high-authority topic clusters, optimize existing content, and position your brand for AI Overviews visibility in 2025–2026.
Start My PASF Growth Strategy✔ Free strategy consultation • ✔ No obligation • ✔ Actionable roadmap included
AI, NLP & Automation: The Future of PASF Research
Manual PASF collection is becoming obsolete. AI and natural language processing are transforming keyword discovery at scale.
How NLP Enables Intent Analysis
Problem: PASF keywords lack intent labels. “Organic face cream” could be informational (learning), commercial (comparing), or transactional (buying).
NLP solution: Machine learning models classify intent by analyzing:
- Keywords themselves (“best,” “buy,” “how to”)
- SERP data (featured snippets signal informational intent)
- User behavior patterns
- Keyword context
Tools using NLP: Semrush, Ahrefs, Nightwatch AI.
Semantic Clustering vs. Traditional Clustering
Traditional approach: Organize keywords by topic
Semantic approach (2025+): Organize keywords by entity and attributes
This aligns with how Google’s Knowledge Graph and Gemini understand topics, improving discoverability in AI-generated answers.
Automation Workflows
Automated PASF pipeline example:
- Daily trigger at 9 AM
- Query SerpApi for top keywords
- Extract PASF results
- Gather search volume via Keyword Planner API
- Output to Google Sheets (automatically updated)
- Outcome: Hands-off keyword database updated weekly
Cost: $50-200/month (eliminates 10+ hours manual work)
Industry-Specific Case Studies: PASF Strategy in Action
Case Study 1: E-Commerce (Fitness Supplements) – 3,480 New First-Page Rankings
Client: Fitness supplement e-commerce site
Baseline: 500 first-page keywords, $15,000/month organic revenue
Goal: Expand long-tail keyword coverage without increasing paid spend
PASF Strategy Executed:
| Phase | Timeline | Action | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Research | Week 1–2 | Collected PASF keywords for 50 primary terms (400+ keywords identified) | Identified 8 major content gaps |
| Planning | Week 3–4 | Created pillar-cluster architecture (5 pillars, 40 clusters) | Content roadmap established |
| Creation | Week 5–12 | Wrote 40 new pages + enhanced 15 existing (600+ hours content) | 9,000 total words new content |
| Optimization | Week 13–16 | Implemented FAQ schema, internal linking, meta optimization | Schema validated, crawlability improved |
| Monitoring | Week 17+ | Tracked rankings, adjusted strategy based on data | Continuous improvement process |
6-Month Results:
| Metric | Baseline | Month 6 | Growth |
|---|---|---|---|
| First-page keywords | 500 | 3,500+ | 600% ↑ |
| Total keywords ranking | 2,100 | 49,848 | 2,270% ↑ |
| Monthly organic traffic | 15,000 | 103,000 | 586% ↑ |
| Organic search revenue | $15,000 | $103,000 | 586% ↑ |
| Average dwell time | 1m 45s | 2m 33s | 42% ↑ |
| Conversion rate | 2.1% | 2.5% | 18% ↑ |
Key success factors:
- PASF keywords revealed lower-competition long-tail opportunities
- Pillar-cluster architecture created topical authority signals
- FAQ schema increased featured snippet capture
- Content addressing PASF intents reduced pogo-sticking
- Semantic consistency across cluster pages strengthened relevance
Case Study 2: SaaS (Project Management Software) – Thought Leadership Positioning
Client: B2B project management SaaS startup
Challenge: Competing against established players (Asana, Monday.com) for SEO visibility
Baseline: 45 keywords ranking, $2,000/month organic lead value
PASF-Driven Strategy:
Focus: Capture long-tail “comparison” and “alternative to” PASF keywords
Example PASF data discovered:
- Primary keyword: “project management software”
- PASF keywords: “best project management software for teams,” “asana vs monday vs notion,” “project management tools for remote teams”
Content approach:
- Created comprehensive comparison articles
- Addressed “versus” PASF keywords with unbiased analysis
- Built thought leadership through detailed feature comparisons
- Implemented FAQ schema for common PASF questions
3-Month Results:
- 240 new keywords ranking (433% growth from baseline)
- $18,500/month organic lead value (825% growth)
- 52% improvement in featured snippet capture
- 85% of new rankings from PASF-derived keywords
Lesson: PASF keywords in competitive niches often have commercial intent; optimizing for them drives higher-quality leads than general topic keywords.
Case Study 3: Health/Wellness Blog – AI Overview Positioning
Client: Nutrition and wellness blog
Challenge: Standing out in crowded health niche; improving visibility in AI-powered search
Baseline: 1,200 keywords ranking, 25,000/month organic traffic
PASF + AI Overview strategy:
- Identified PASF keywords with high AI Override potential
- Created definitive, cited-source content addressing those keywords
- Implemented full schema markup (HowTo, Article, FAQ, Organization)
- Built topical authority around wellness topics using cluster strategy
- Optimized for snippet capture with 40-60 word answer placement
Example PASF keywords targeted:
- “best supplements for energy”
- “natural energy boosters science-backed”
- “supplements vs caffeine effectiveness”
6-Month Results:
- 2,840 new keywords ranking (137% growth)
- 68,000/month organic traffic (172% growth)
- 18 pages cited in Google AI Overviews (major milestone)
- 35% increase in health practitioner partnerships (via increased credibility)
Key insight: Health/wellness content optimized for PASF and schema markup performs exceptionally well in AI Overviews due to topical authority and cited-source positioning.
PASF SEO Strategy in 2025–2026: Adapting to AI-Powered Search
From Keyword Rankings to AI Override Sources
2023 Reality: Rank in position #1, capture clicks
2025–2026 Reality: Rank in position #1 AND be cited in AI Overviews
PASF keywords often represent information gaps that AI Overviews must address. By addressing these gaps comprehensively, you increase citation likelihood in AI-generated answers.
Entity-Based Content vs. Keyword-Based
Shift: From targeting isolated keywords → mapping semantic entity relationships
Use schema markup to clarify entity relationships (Product, Organization, BreadcrumbList) rather than relying on keyword matching alone.
Semantic Clustering Over Traditional Topics
Traditional clustering groups by topic; semantic clustering organizes by entity attributes and relationships aligning with how Google’s Knowledge Graph understands information.
Implementation Roadmap: From Zero to PASF Mastery
For Individual Content Creators (1–5 Pages)
Timeline: 4–8 hours per page
- Manual PASF discovery (search, click, note keywords)
- Content audit (check PASF coverage)
- Add H2/H3 sections for missing keywords
- Implement FAQ schema
- Internal linking to related pages
Expected result: 30–50% keyword coverage improvement
For Small SEO Teams (10–50 Pages)
Timeline: ~300 hours over 3 months
- Install Keywords Everywhere ($10-20/month)
- Build PASF database for top 20 keywords
- Create pillar-cluster content map
- Develop 3–5 pillar pages
- Create 15–30 cluster pages
- Implement full schema markup
- Monitor and iterate
Expected result: 500–2,000 new page-1 keywords within 6 months
For Enterprise Programs (100+ Pages)
Timeline: 750+ hours setup; 100+ hours monthly maintenance
- Automate PASF collection (SerpApi)
- AI-powered semantic clustering
- Develop 10–20 pillar pages with 50–200 clusters
- Implement comprehensive schema
- Build monitoring dashboard
- Continuous optimization cycle
Expected result: 5,000+ new page-1 keywords; 300%+ organic traffic growth
Conclusion
People Also Search For represents one of the most underutilized, high-leverage opportunities in modern SEO. While competitors chase paid keywords and paid traffic, you can build sustainable, compounding organic growth by answering the questions Google is literally showing you users want answered a strategy actively leveraged by devtrios.com.
The advantages:
- Data-driven (from Google’s actual user data)
- Low competition (most competitors ignore PASF)
- High intent (users actively seeking information)
- Scalable (can be automated)
- Future-proof (drives AI Override citations)
Your next steps:
- This week: Manually collect PASF keywords for 5 target queries
- Next week: Install Keywords Everywhere, audit current content gaps
- Month 1: Build pillar-cluster content map
- Month 2-3: Create optimized content addressing PASF keywords
- Month 3+: Monitor, refine, scale
The case studies in this guide aren’t luck they’re the result of systematically understanding user intent, addressing content gaps, and building topical authority around keywords users actually search for.
The question isn’t whether to use PASF. The question is whether you’ll implement it before your competitors do.
Ready to Turn People Also Search For Data Into Rankings?
If you're serious about scaling organic traffic and capturing high-intent search opportunities, People Also Search For (PASF) data gives you a direct window into real user behavior. Our SEO specialists help you uncover hidden keyword gaps, build authority-driven topic clusters, optimize existing content, and position your site for featured snippets and AI Overviews in 2025–2026.
Start My PASF SEO Strategy →Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
PASF appears when a user clicks on a search result and quickly returns to Google (pogo-sticking behavior). Google interprets this as a signal that the user didn't find what they needed. The system then displays 6–8 related queries that other users have searched for after visiting that same result. PASF relies on aggregated user behavior data, not predictive algorithms.
PASF data updates dynamically and continuously. Each PASF box reflects recent user behavior for that specific result. Because PASF is user-triggered and behavior-based, it changes moment-to-moment based on who's searching and bouncing. There's no fixed refresh schedule; Google processes PASF in real-time.
No, you cannot directly rank "in" PASF like you can with featured snippets or PAA boxes. PASF is not a ranking position; it's a collection of alternate search queries. However, optimizing for PASF-derived keywords improves your chances of ranking for those keywords in traditional organic results, and addressing PASF keywords often triggers featured snippet opportunities.
Scraping PASF data exists in legal gray area. While courts ruled that scraping publicly available data is legal (hiQ Labs v. LinkedIn, 2019), Google forbids it in its ToS. You may face temporary IP blocks, but legal action is rare. For compliance, use official tools (Semrush, Ahrefs, Keywords Everywhere) or implement rate-limited scraping with proxies.
PASF shows related search queries appearing after a user bounces from a result, while PAA shows question-and-answer boxes displayed in the SERP. PASF is keyword-focused; PAA is question-focused. Both reveal user intent but through different mechanisms.
PASF doesn't directly affect rankings. However, the user behavior triggering PASF pogo-sticking can indirectly impact rankings. If your page causes repeated bounces (short clicks), Google's algorithm may reduce your ranking. Optimizing for PASF keywords improves content-query match, reducing pogo-sticking and strengthening rankings.
Manually search your target keyword on Google, click a result, and hit the back button. Note all 6–8 PASF keywords shown. Repeat for multiple results. For scale, use Keywords Everywhere extension (~$10/month). Manual collection is free but time-intensive (5-10 minutes per keyword).
Semrush Keyword Magic Tool offers the best balance of PASF data, intent classification, and team collaboration. For budget-conscious teams, Keywords Everywhere provides solid volume/difficulty data at lower cost. For competitive intelligence, Ahrefs Keyword Generator excels.
Address 3–8 PASF keyword variations per page. Create main content targeting your primary keyword, then add H2/H3 sections for 3–5 related PASF keywords with significant volume. Bundle low-volume keywords into FAQ sections.
Yes, PASF data is highly localized. Different regions show different PASF keywords based on local user behavior and language. When targeting international audiences, collect region-specific PASF data using location-targeted searches with VPNs.
Absolutely. Adding PASF-derived keywords as new H2/H3 sections to existing content is one of the fastest ways to improve rankings. This "content optimization" approach improves existing page rankings by increasing relevance, depth, and engagement.
PASF data represents information gaps that AI Overviews must fill. Content optimized for PASF keywords has higher chances of being cited by Gemini and other AI systems. In 2025–2026, the strategy shifts from "rank in featured snippets" to "be cited in AI Overviews," with PASF data guiding this shift.
About the Author
This article is written by Ali Hamza, a digital strategist and technology writer with hands-on experience in product development, emerging technologies, SEO, and scalable digital systems. He focuses on translating complex technical topics into clear, practical guidance that helps readers make informed decisions.
Ali regularly researches consumer technology trends, software platforms, and digital optimization strategies, ensuring content accuracy, usability, and real-world relevance across a wide range of topics.
View Author Profile →




